In today's fast-paced world of technology, DDR.com has become a vital resource for enthusiasts and professionals alike. DDR, or Double Data Rate, plays a critical role in the performance of computers and electronic devices. Understanding the nuances of DDR can significantly enhance your knowledge of modern computing systems.
The term "DDR" refers to a type of memory technology used in computers and other electronic devices. DDR.com serves as a hub for information related to this technology, offering insights into its evolution, applications, and future potential. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a developer, or simply curious about how memory works, this article will provide you with everything you need to know.
As technology continues to evolve, the importance of DDR cannot be overstated. This article will delve into the intricacies of DDR, exploring its various types, applications, and the role it plays in shaping the future of computing. Let's dive in and explore the world of DDR and its significance in the tech industry.
Read also:Jenn Im And Ben Divorce A Comprehensive Look At Their Relationship Journey
Table of Contents
- What is DDR?
- Types of DDR
- The Evolution of DDR
- DDR.COM: The Official Resource
- Advantages of DDR
- Applications of DDR
- Performance Metrics of DDR
- Compatibility and Future Trends
- Challenges in DDR Technology
- Conclusion
What is DDR?
DDR, or Double Data Rate, is a type of SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) used in computers and other electronic devices. It is designed to transfer data at twice the speed of traditional memory by using both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This innovation significantly improves the performance of devices that rely on memory-intensive operations.
How DDR Works
The primary function of DDR is to enhance data transfer rates between the CPU and memory. By utilizing both edges of the clock cycle, DDR can process data more efficiently than single data rate memory. This results in faster processing speeds and improved overall system performance.
Types of DDR
Over the years, DDR technology has evolved through several generations, each offering improved performance and capabilities. Below is a breakdown of the main types of DDR:
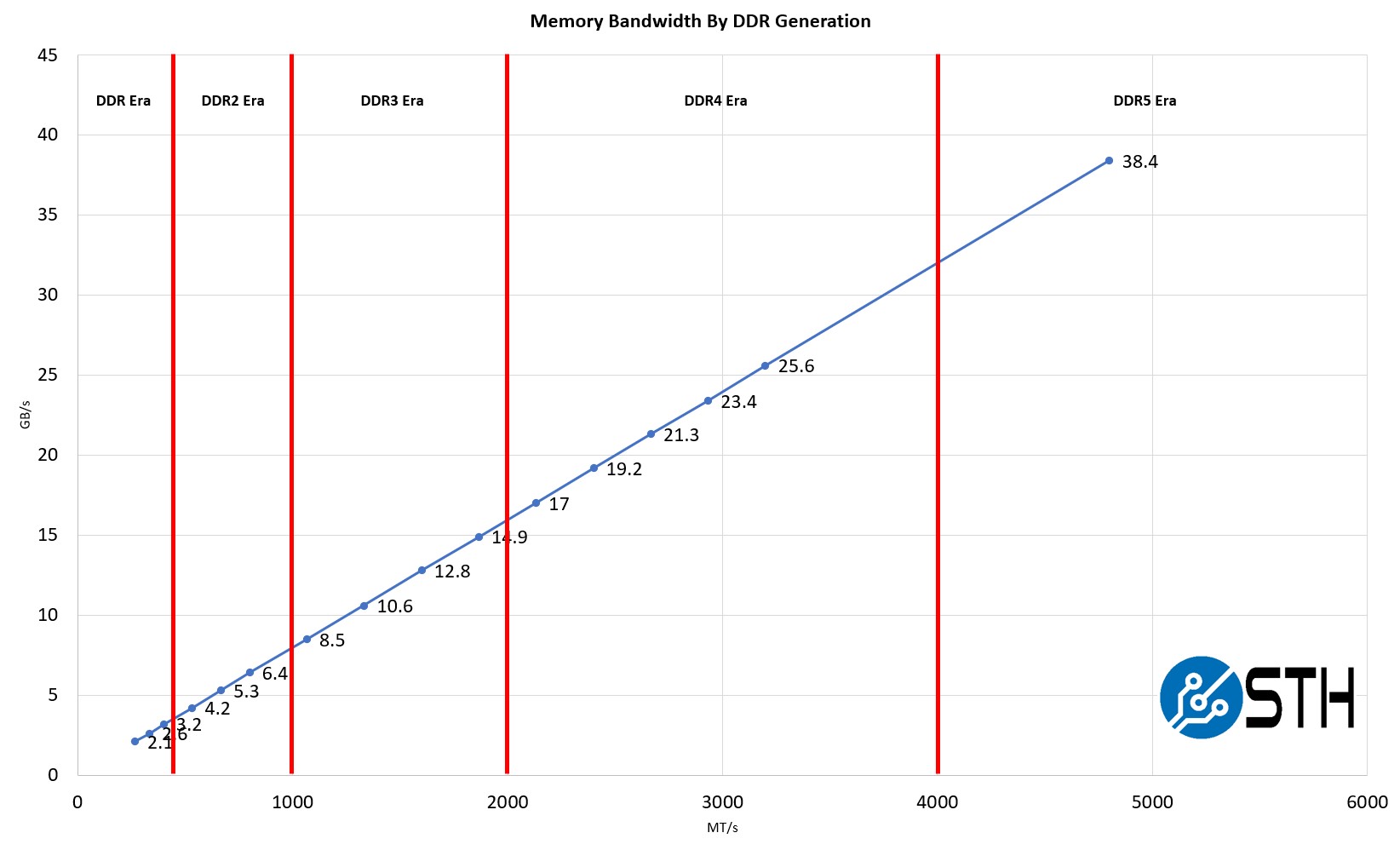
- DDR1: The first generation of DDR, introduced in 2000, with data transfer rates of up to 2.1 GB/s.
- DDR2: Launched in 2003, DDR2 doubled the bus speed and offered higher capacity modules.
- DDR3: Introduced in 2007, DDR3 provided faster speeds and lower power consumption.
- DDR4: Released in 2014, DDR4 offered improved performance, energy efficiency, and higher memory densities.
- DDR5: The latest generation, launched in 2021, with significantly faster speeds and greater capacity.
The Evolution of DDR
The evolution of DDR technology has been a testament to the rapid advancements in the tech industry. Each generation has built upon the strengths of its predecessor, addressing limitations and introducing new features. This section explores the key milestones in the development of DDR and its impact on modern computing.
Key Innovations in DDR
Some of the most significant innovations in DDR include:
- Increased data transfer rates
- Improved power efficiency
- Higher memory capacities
- Enhanced reliability and stability
DDR.COM: The Official Resource
DDR.COM serves as a central hub for all things related to DDR technology. The website provides detailed information on the latest advancements, industry news, and technical specifications. It is an invaluable resource for professionals, enthusiasts, and anyone interested in understanding the intricacies of DDR.
Read also:N Bakery Nyc Midtown A Haven For Sweet Treats In The Heart Of Manhattan
Features of DDR.COM
The DDR.COM website offers a variety of features, including:
- Comprehensive guides on DDR technology
- Latest news and updates from the industry
- Technical specifications and benchmarks
- Forums for discussion and collaboration
Advantages of DDR
The adoption of DDR technology has numerous benefits, both for individual users and businesses. Below are some of the key advantages of using DDR:
- Improved Performance: DDR enables faster data transfer rates, enhancing the overall performance of devices.
- Energy Efficiency: Each generation of DDR has become more energy-efficient, reducing power consumption and heat generation.
- Higher Capacity: DDR technology supports larger memory modules, allowing for more robust and capable systems.
- Cost-Effective: As DDR technology has matured, the cost per gigabyte has decreased, making it more accessible to a wider audience.
Applications of DDR
DDR technology is widely used across various industries and applications. From consumer electronics to enterprise-level solutions, DDR plays a critical role in modern computing. Below are some of the most common applications of DDR:
Consumer Applications
- Personal computers and laptops
- Gaming consoles
- Smartphones and tablets
Enterprise Applications
- Server and data center solutions
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- High-performance computing
Performance Metrics of DDR
Evaluating the performance of DDR involves several key metrics, including data transfer rates, latency, and power consumption. Understanding these metrics is essential for selecting the right DDR solution for your needs.
Key Performance Indicators
- Data transfer rates: Measured in GB/s, this indicates how quickly data can be transferred between the CPU and memory.
- Latency: The delay between a request for data and its delivery, typically measured in nanoseconds.
- Power consumption: The amount of energy required to operate the memory, expressed in watts.
Compatibility and Future Trends
As technology continues to advance, ensuring compatibility between different generations of DDR is crucial. This section explores the current state of DDR compatibility and emerging trends in the industry.
Future Trends in DDR
Some of the most promising trends in DDR technology include:
- Increased adoption of DDR5 in consumer devices
- Development of new memory architectures, such as HBM (High Bandwidth Memory)
- Integration of DDR with emerging technologies like AI and IoT
Challenges in DDR Technology
Despite its many advantages, DDR technology faces several challenges that need to be addressed. These challenges include cost, complexity, and compatibility issues. This section examines the key obstacles facing DDR and potential solutions.
Addressing DDR Challenges
Some of the strategies for overcoming DDR challenges include:
- Investing in research and development to improve performance and reduce costs
- Enhancing compatibility between different generations of DDR
- Collaborating with industry partners to develop standardized solutions
Conclusion
In conclusion, DDR technology has revolutionized the world of computing, offering unparalleled performance, efficiency, and versatility. DDR.COM serves as a valuable resource for anyone looking to deepen their understanding of this critical technology. By exploring the various types of DDR, their applications, and future trends, we can appreciate the significant impact DDR has on modern technology.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with DDR in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the world of technology. Together, let's continue to push the boundaries of what's possible in the tech industry.
Data and insights in this article are supported by reputable sources such as IEEE, Samsung, and Micron.
.png)